We are excited to announce the second release of PyCaret today.
PyCaret is an open source, low-code machine learning library in Python that automates machine learning workflow. It is an end-to-end machine learning and model management tool that speeds up machine learning experiment cycle and makes you more productive.
In comparison with the other open source machine learning libraries, PyCaret is an alternate low-code library that can be used to replace hundreds of lines of code with few words only. This makes experiments exponentially fast and efficient.
See detailed release notes for PyCaret 2.0.
Why use PyCaret?

Installing PyCaret 2.0
Installing PyCaret is very easy and takes only a few minutes. We strongly recommend using virtual environment to avoid potential conflict with other libraries. See the following example code to create a conda environment and install pycaret within that conda environment:
# create a conda environment
conda create --name yourenvname python=3.6 # activate environment
conda activate yourenvname # install pycaret
pip install pycaret==2.0 # create notebook kernel linked with the conda environment python -m ipykernel install --user --name yourenvname --display-name "display-name"
If you are using Azure notebooks or Google Colab, run the following code to install PyCaret.
!pip install pycaret==2.0All hard dependencies are automatically installed when you install PyCaret using pip. Click here to see the complete list of dependencies.
👉 Getting Started with PyCaret 2.0
The first step of any machine learning experiment in PyCaret is to set up an environment by importing the relevant module and initialize the setup function by passing dataframe and name of the target variable. See example code:
Sample Output:

All the preprocessing transformations are applied within setup function. PyCaret provides over 20 different pre-processing transformation that can be defined within setup function. Click here to learn more about PyCaret’s preprocessing abilities.

👉 Compare Models
This is the first step we recommend in any supervised machine learning task. This function trains all the models in the model library using default hyperparameters and evaluates performance metrics using cross validation. It returns the trained model object class. The evaluation metrics used are:
- For Classification: Accuracy, AUC, Recall, Precision, F1, Kappa, MCC
- For Regression: MAE, MSE, RMSE, R2, RMSLE, MAPE
Here are few ways you can use compare_models function:
Sample Output:
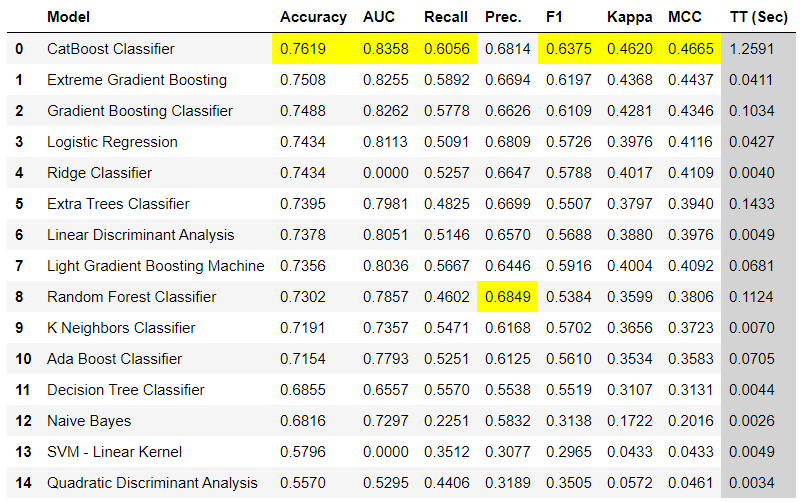
👉 Create Model
Create Model function trains a model using default hyperparameters and evaluates performance metrics using cross validation. This function is base to almost all other functions in PyCaret. It returns the trained model object class. Here are few ways you can use this function:
Sample Output:
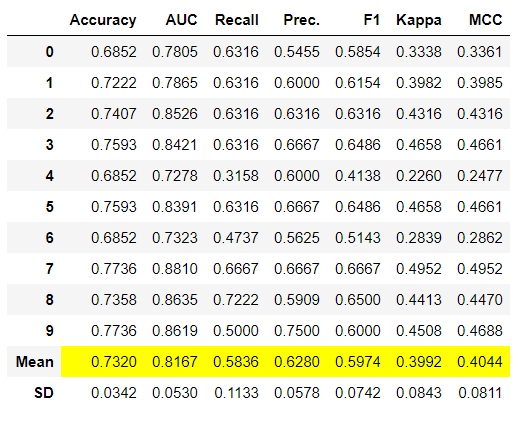
To learn more about create model function, click here.
👉 Tune Model
Tune Model function tunes the hyperparameter of the model passed as an estimator. It uses Random grid search with pre-defined tuning grids that are fully customizable. Here are few ways you can use this function:
To learn more about tune model function, click here.
👉 Ensemble Model
There are few functions available to ensemble base learners. ensemble_model, blend_models and stack_models are three of them. Here are few ways you can use this function:
To learn more about ensemble models in PyCaret, click here.
👉 Predict Model
As the name suggests, this function is used for inference / prediction. Here is how you can use it:
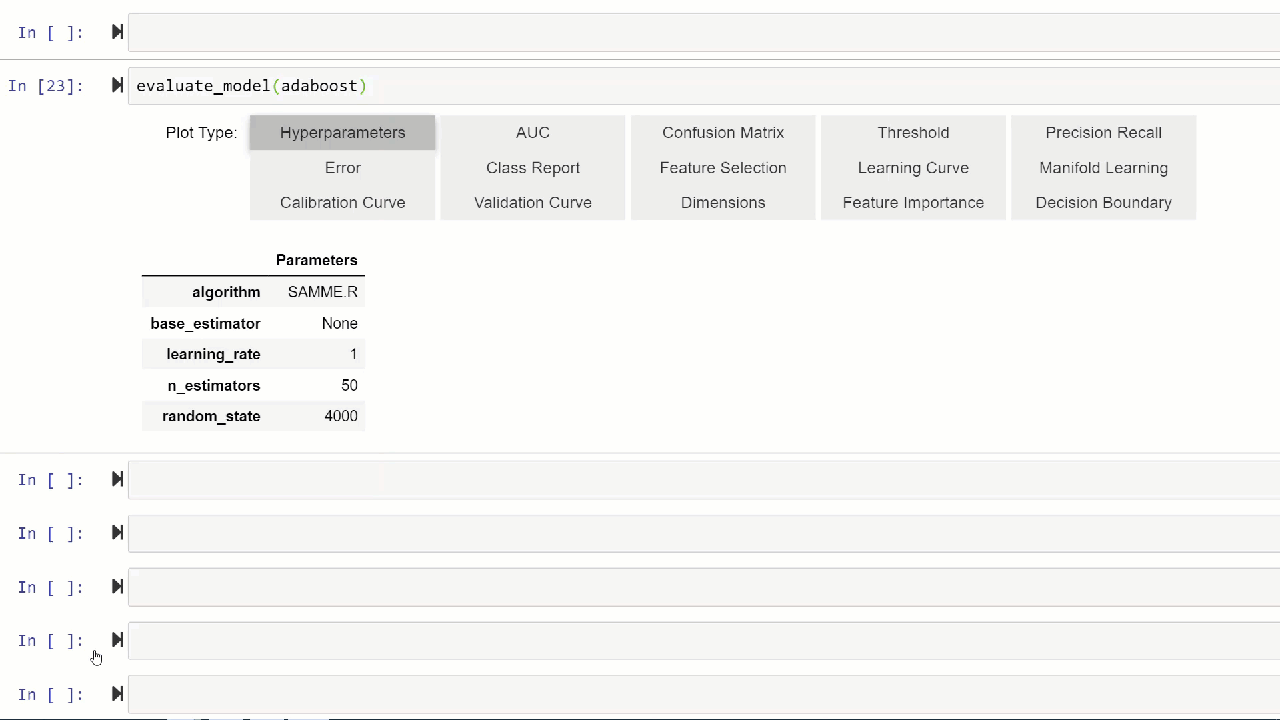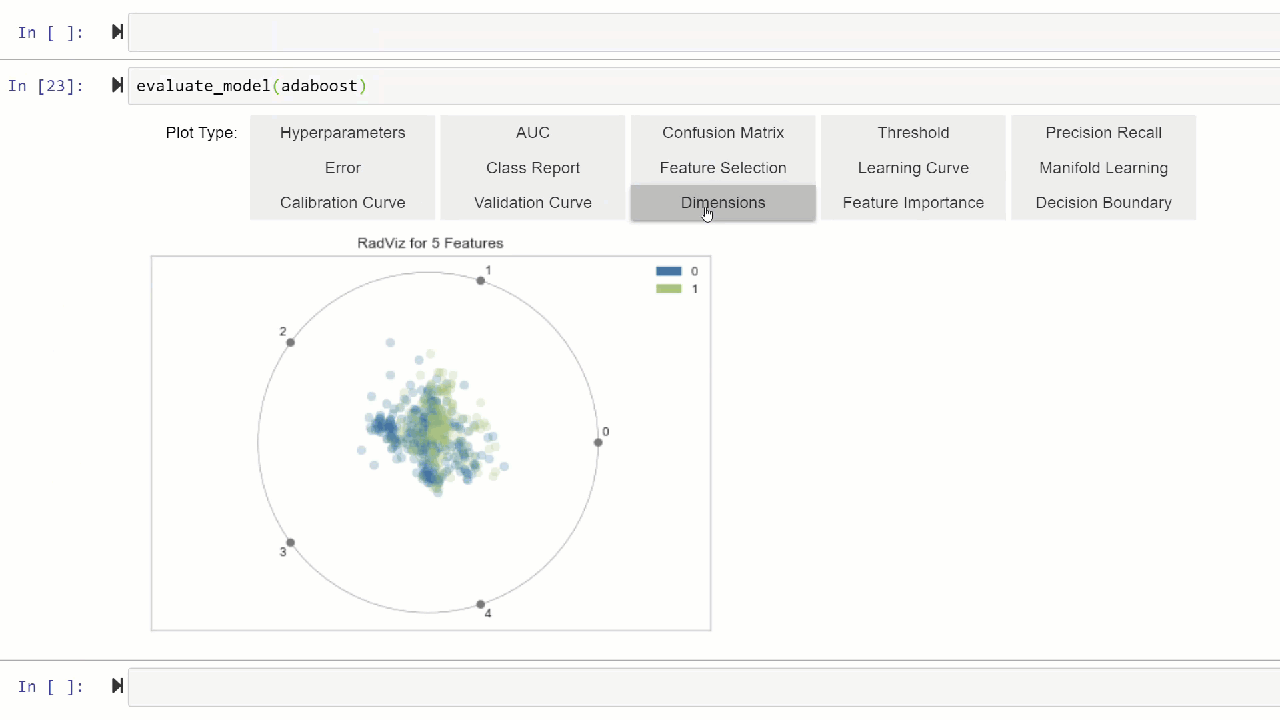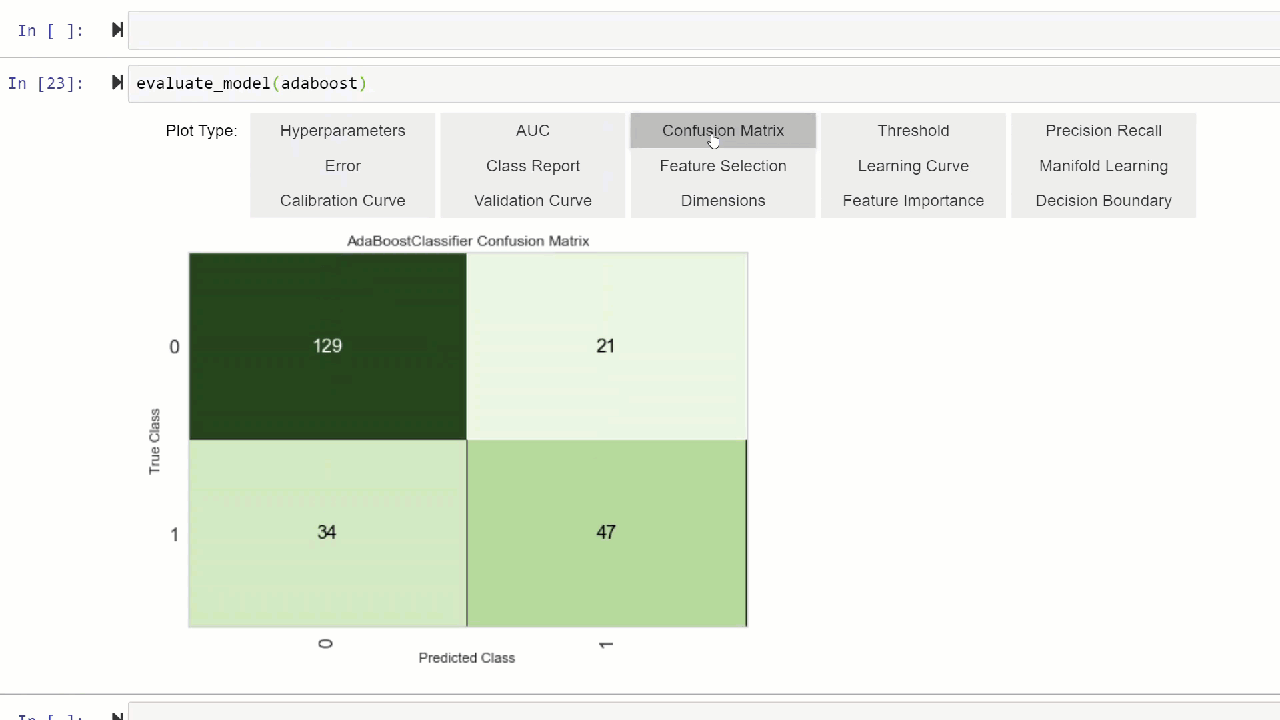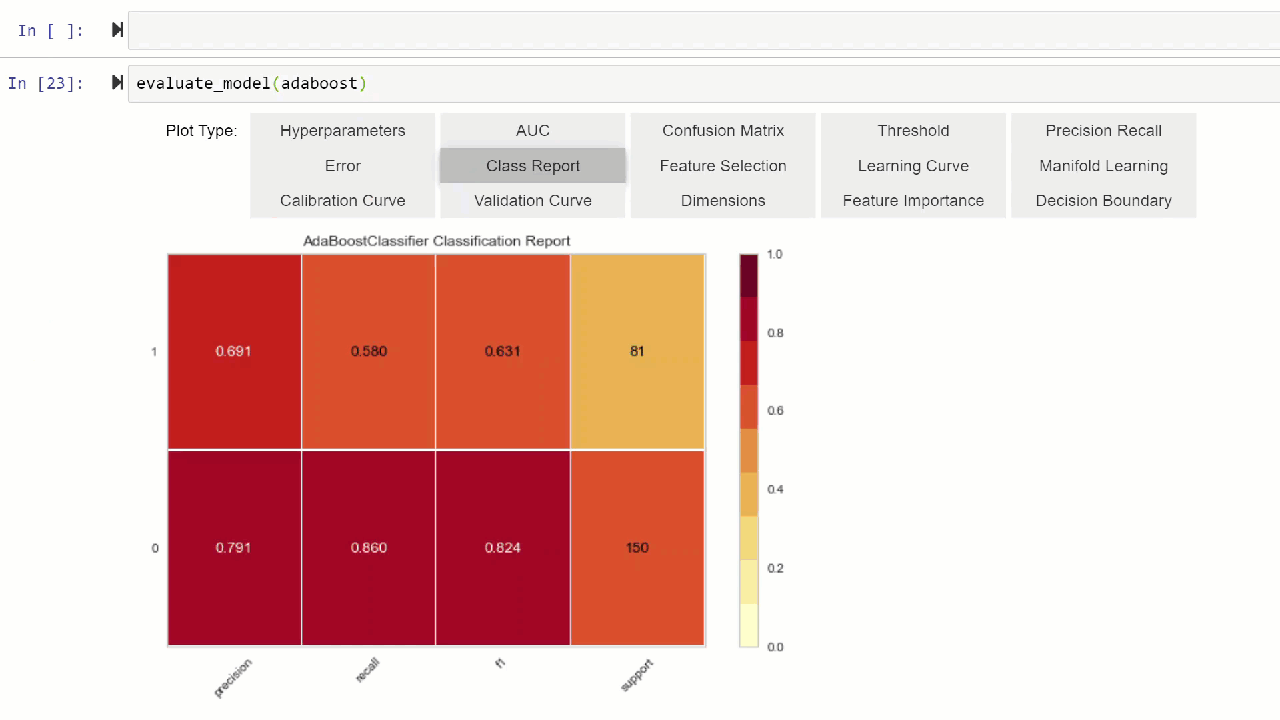
👉 Plot Model
Plot Model function is used to evaluate performance of the trained machine learning model. Here is an example:
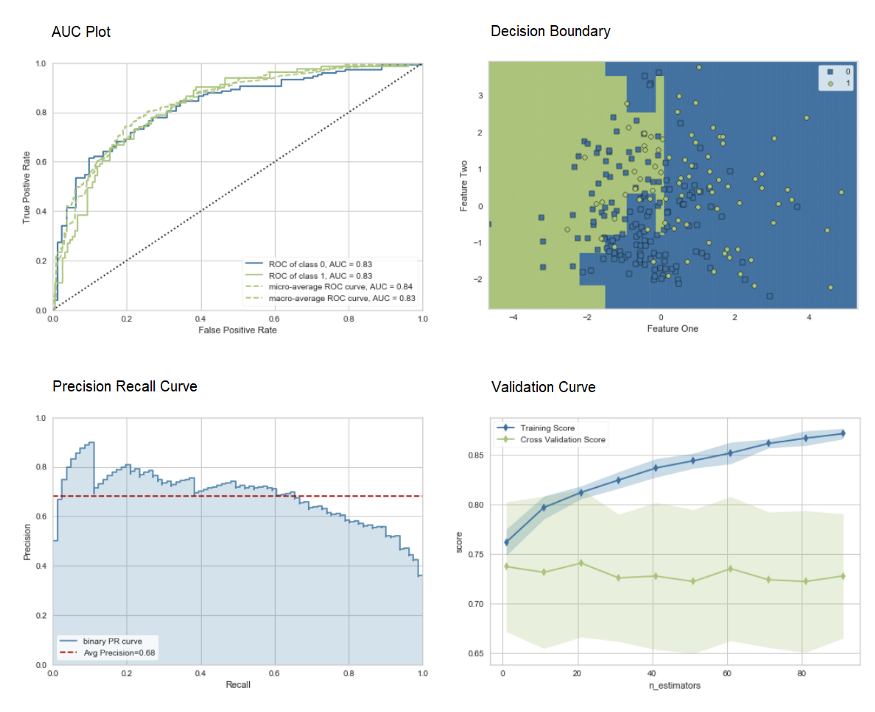
Click here to learn more about different visualization in PyCaret.
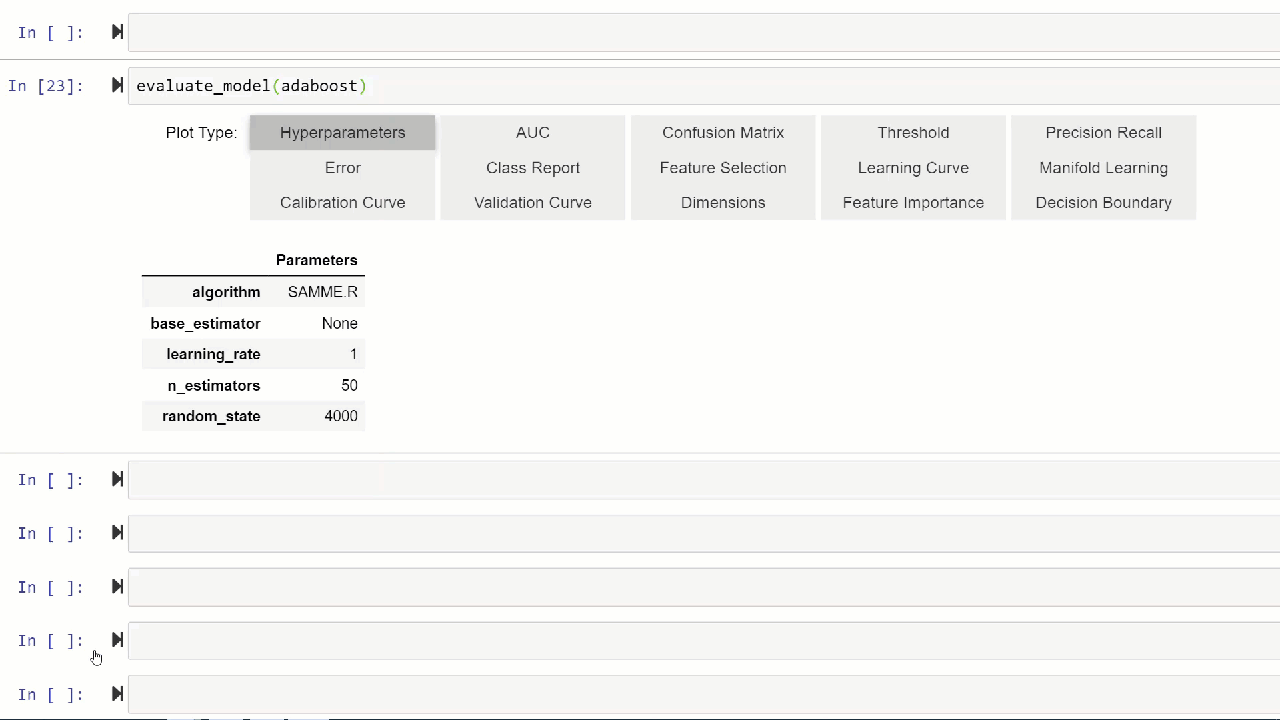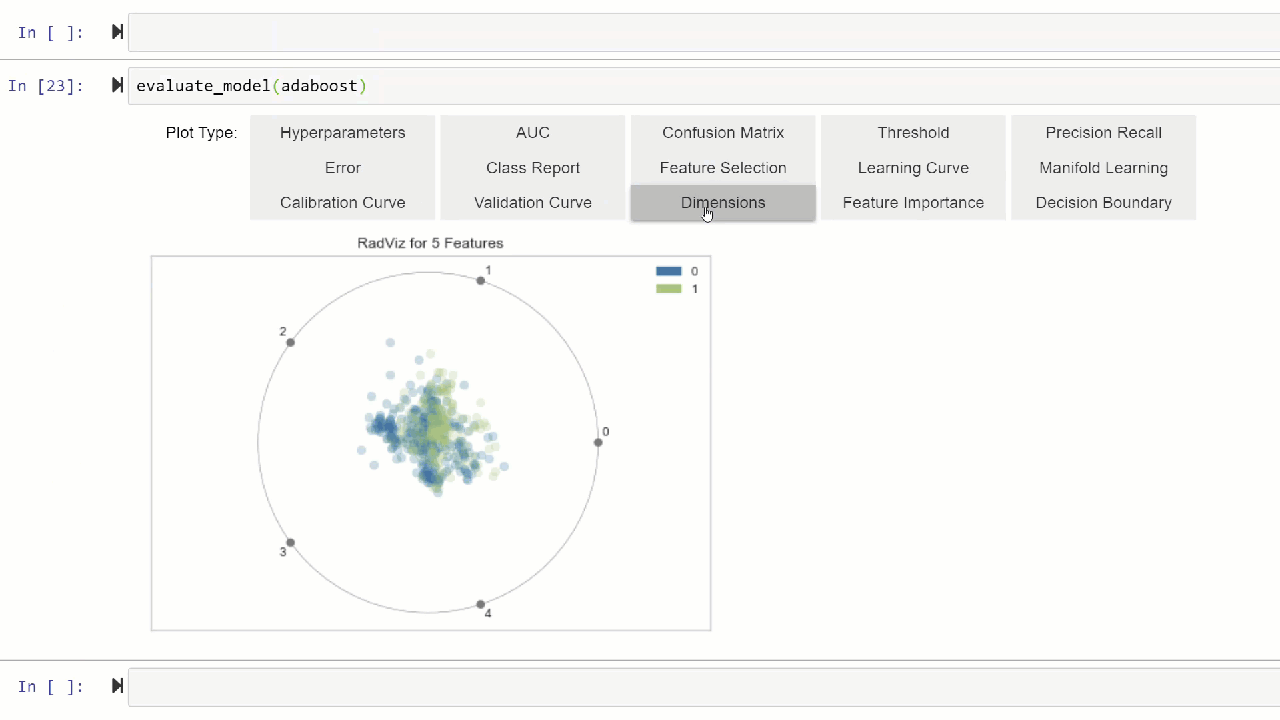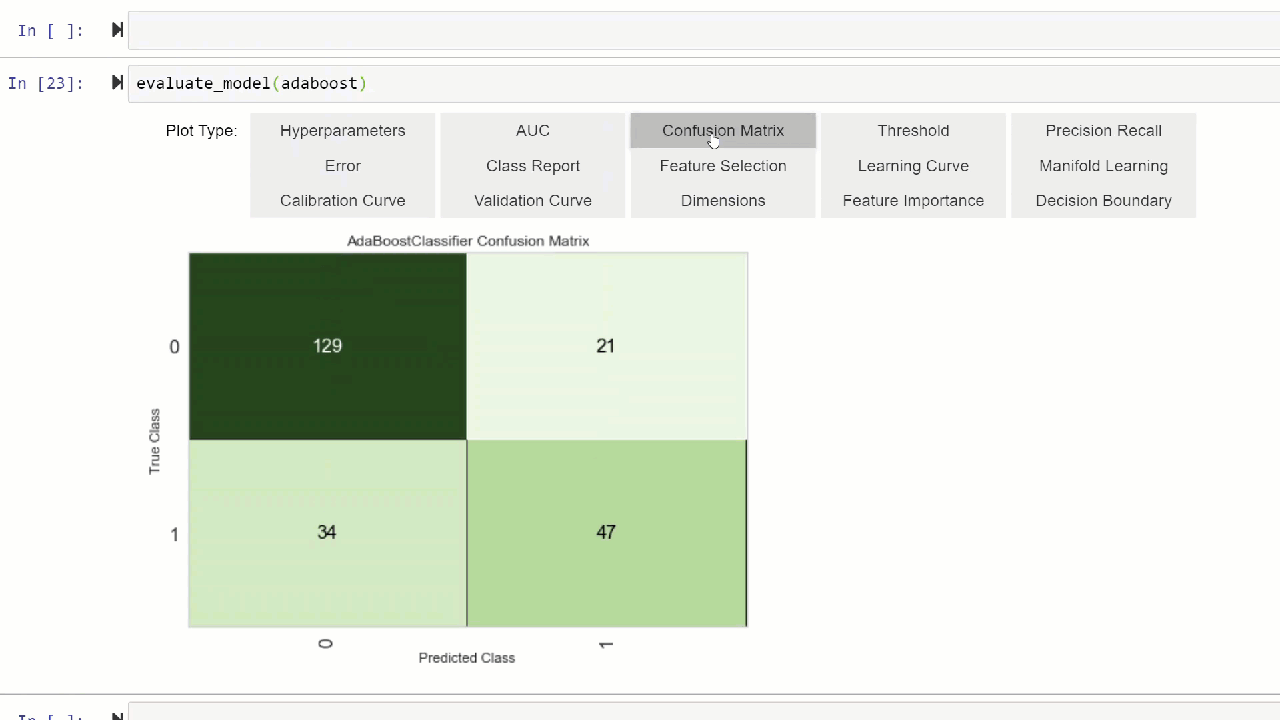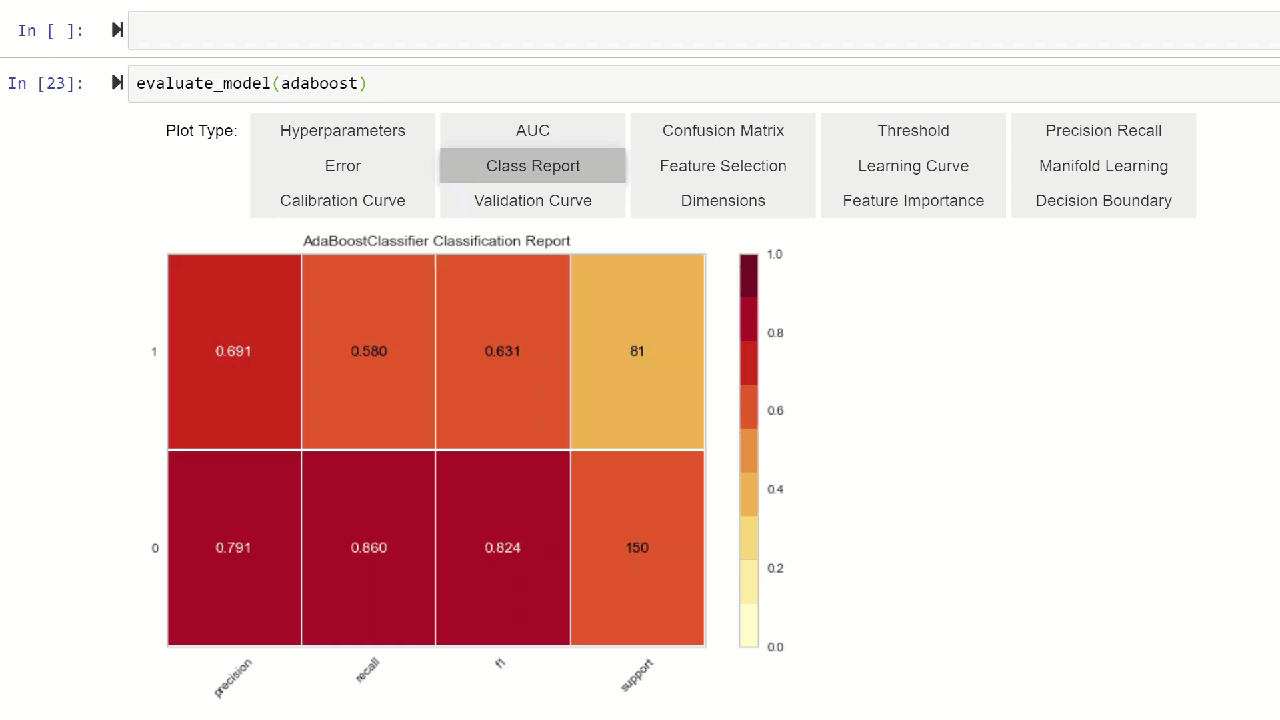
Alternatively, you can use evaluate_model function to see plots via the user interface within notebook.
👉 Util functions
PyCaret 2.0 includes several new util functions that comes handy when managing your machine learning experiments with PyCaret. Some of them are shown below:
To see all new functions implemented in PyCaret 2.0, See release notes.
👉 Experiment Logging
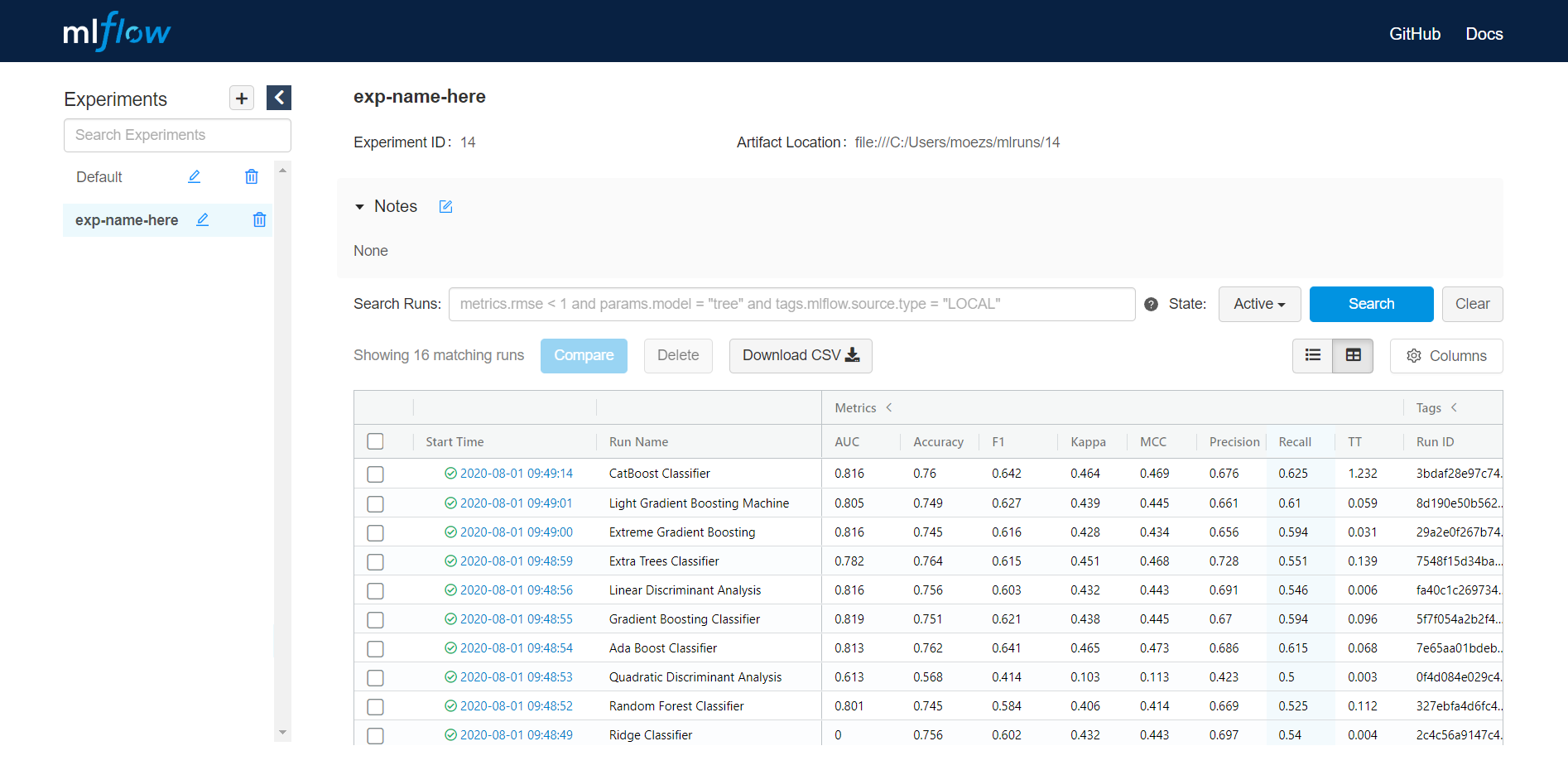
PyCaret 2.0 embeds MLflow tracking component as a backend API and UI for logging parameters, code versions, metrics, and output files when running your machine learning code and for later visualizing the results. Here is how you can log your experiment in PyCaret.
Output (on localhost:5000)
👉 Putting it all together — Create your own AutoML software
Using all the functions, let’s create a simple command line software that will train multiple models with default parameters, tune hyperparameters of top candidate models, try different ensembling techniques and returns / saves the best model. Here is the command line script:
This script will dynamically select and saves the best model. In just few lines of code you have developed your own Auto ML software with a full fledged logging system and even a UI presenting beautiful leaderboard.
There is no limit to what you can achieve using the light weight workflow automation library in Python. If you find this useful, please do not forget to give us ⭐️ on our github repo if you like PyCaret.
To hear more about PyCaret follow us on LinkedIn and Youtube.
Important Links
Release Notes for PyCaret 2.0
User Guide / Documentation
Github
Install PyCaret
Notebook Tutorials
Contribute in PyCaret
Want to learn about a specific module?
Click on the links below to see the documentation and working examples.
Classification
Regression
Clustering
Anomaly Detection
Natural Language Processing
Association Rule Mining
WRITTEN BY






No comments:
Post a Comment