OOW’19 stands up from recent years OOW conferences with important announcement — Oracle Cloud Free Tier offering. This offering includes two free DB instances and two free compute VM instances. What else you could wish for the side and hobby projects? This is a strong move by Oracle and it should boost Oracle Cloud. Read more about it in Oracle Cloud Free Tier page.
It was interesting to test how to deploy Oracle JET app to Oracle Always Free instance of compute VM. I will not go through the initial steps, related how to create VM instance and enable internet access (for the port 80). You can read all that in a nice write up from Dimitri Gielis post.
Assuming you already have created Oracle JET app and want to deploy it. One way would be to set up Node.js and Nginx on the compute VM and pull app source code from Git. I prefer another way — to go through Docker container, Nginx would act as an HTTP server to redirect requests to Docker container port. But in this post for simplicity reasons, we are not going to look into Nginx setup — will focus only on JET deployment through Docker container.
1. Create an empty Node application (follow these steps):
express — view=pug
2. Add dependencies, go into the Node app and run:
npm install
3. Copy Oracle JET content from web folder into Node app public folder (remove existing files)
4. Inside the Node app, adjust app.js file, comment out these lines:
var usersRouter = require(‘./routes/users’);app.set(‘view engine’, ‘pug’);app.use(‘/users’, usersRouter);
5. Keep only index.js file in router folder
6. Remove template files from views folder
7. Update index.js file to redirect to Oracle JET index.html
router.get(‘/’, function(req, res, next) {
//res.render(‘index’, { title: ‘Express’ });
res.sendFile(‘index.html’, {root: ‘./public/’});
});
8. Note down port 3000 info from bin/www, this is the port Node app will run in Docker container
9. Create Dockerfile inside Node app folder (follow these steps). Content:
FROM node:10# Create app directory WORKDIR /usr/src/app# Install app dependencies # A wildcard is used to ensure both package.json AND package-lock.json are copied # where available (npm@5+) COPY package*.json ./RUN npm install # If you are building your code for production # RUN npm ci — only=production# Bundle app source COPY . .EXPOSE 3000 CMD [ “node”, “./bin/www” ]
10. Create .dockerignore file. Content:
node_modules
npm-debug.log
11. Build a Docker image locally, by running below command inside the Node app:
docker build -t username/imagename -f ./Dockerfile .
12. Push Docker container to Docker Hub. This way we will be able to pull the container from Oracle compute VM in the cloud:
docker push username/imagename
— — — — — — —
Next steps are executed inside Oracle compute VM. You should connect through SSH to run below commands.
13. Install Docker (run sudo su):
yum install docker-engine
14. Enable Docker:
systemctl enable docker
15. Start Docker:
systemctl start docker
16. Check Docker status:
systemctl status docker.service
17. Check Docker version:
docker version
18. Login into Docker Hub, to be able to pull the container with Node app. If login doesn’t work (access permission issue), run this command: sudo usermod -a -G docker $USER
docker login
19. Run container:
docker run -p 80:3000 -d — name appname username/imagename
Node app with Oracle JET content can be accessed by port 80 using public IP of your Oracle container VM: http://130.61.241.30/index.html
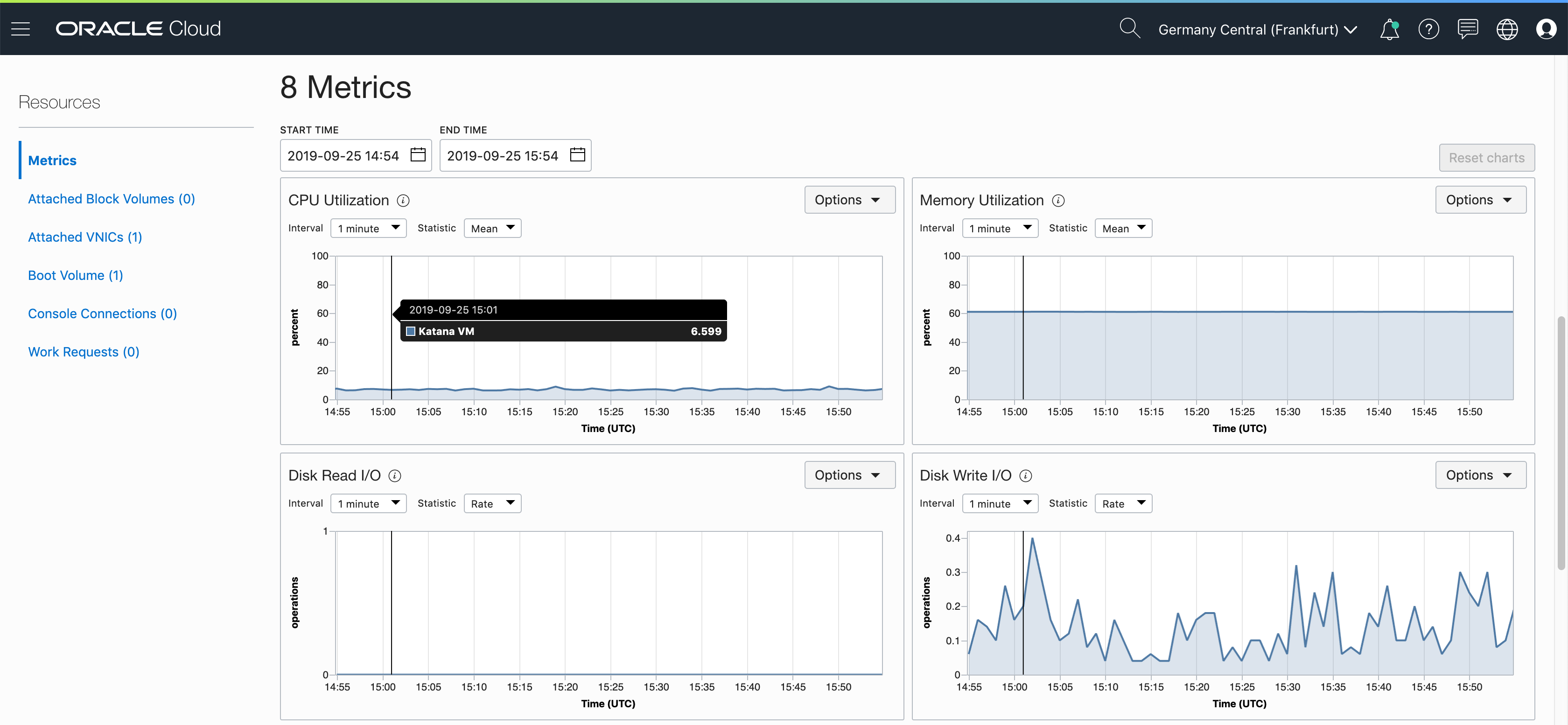
Oracle JET app runs on Oracle container VM free tier:

Originally published at http://andrejusb.blogspot.com.


No comments:
Post a Comment